Installation
1. Open the terminal by Ctrl+Alt+T
and type
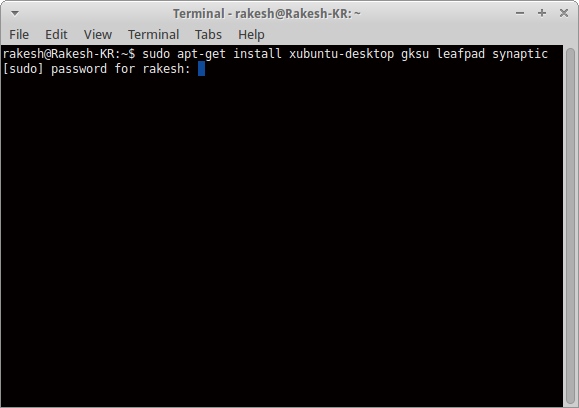
sudo apt-get install xubuntu-desktop gksu leafpad synaptic
1. Open the terminal by Ctrl+Alt+T
and type
sudo apt-get install xubuntu-desktop gksu leafpad synaptic
2. Type your password & Press Enter. Now an intensive operation is being launched. Simply wait to complete the whole process.
Login To Xubuntu
1. After completing the installation logout ubuntu. Note: logout not restart or shutdown.
2. In the login window click on the ubuntu logo, next to your userName & select Xubuntu Sesion
3. Enter your password and Now the Xubuntu desktop appears. :) The next thing is to clean up.
Clean Up
1. Now its time to clean up, inorder to prevent system pollution problems.
Note: The clean up will remove as much as possible ubuntu's desktop environment Unity. So after that you can't use Unity.
2. Open terminal by Ctrl+Alt+T and type the following
sudo apt-get remove nautilus gnome-power-manager gnome-screensaver gnome-termina* gnome-pane* gnome-applet* gnome-bluetooth gnome-desktop* gnome-sessio* gnome-user* gnome-shell-common compiz compiz* unity unity* hud zeitgeist zeitgeist* python-zeitgeist libzeitgeist* activity-log-manager-common gnome-control-center gnome-screenshot overlay-scrollba* && sudo apt-get install xubuntu-community-wallpapers && sudo apt-get autoremove
3. Press Enter & Type your password. You are almost done now. Reboot your computer & Enjoy.

Comments
Post a Comment